The phosphate rocks market is an essential part of the global agricultural and industrial supply chain. As a primary source of phosphorus, phosphate rocks are indispensable for the production of phosphate fertilizers, which in turn play a crucial role in ensuring food security worldwide. Over the past few decades, the market has grown in response to rising population levels, increasing food demand, and expanding industrial applications. The phosphate rocks market continues to evolve due to changing agricultural practices, resource availability, geopolitical factors, and environmental concerns.
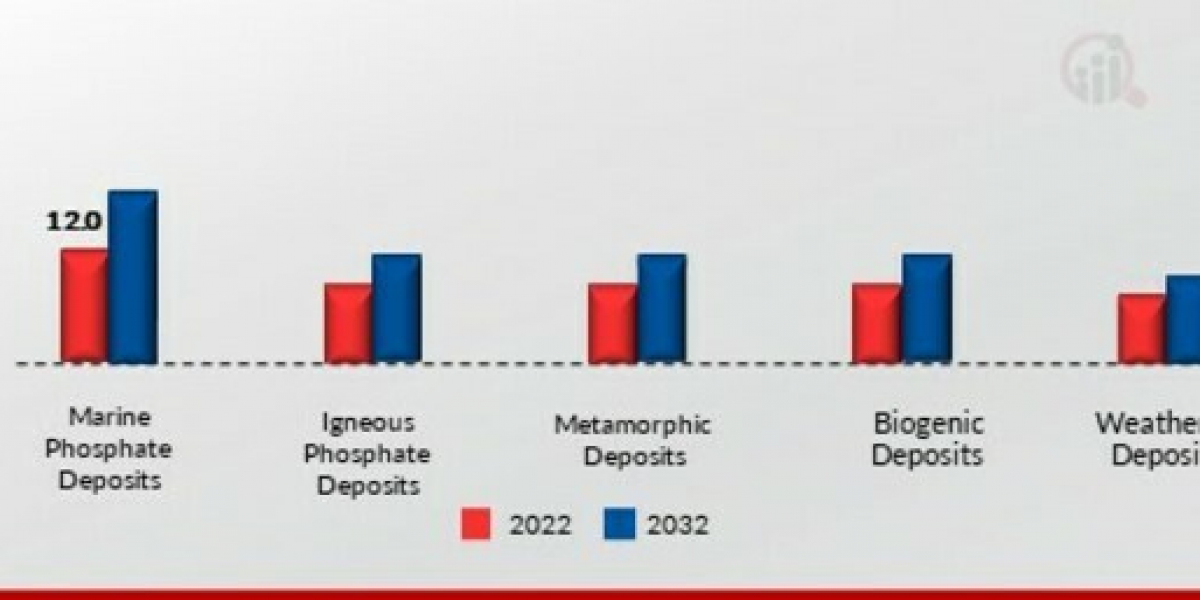
Phosphate rock is a sedimentary rock containing high amounts of phosphate minerals, typically apatite. These rocks are mined, crushed, and processed to extract phosphorus, which is used in fertilizers, animal feed, and various chemical products. Fertilizer production remains the dominant use of phosphate rocks, accounting for the majority of global consumption. The demand is driven mainly by countries with large agricultural economies or limited domestic reserves of phosphorus-rich rock.
Globally, the largest producers of phosphate rock include China, the United States, Morocco, and Russia. Among these, Morocco is home to the world’s largest phosphate reserves, making it a central player in the international market. China, on the other hand, leads in overall production and consumption, driven by its vast agricultural sector. The U.S. and Russia also contribute significantly, both in production and in the development of processing technologies.
The market is segmented based on application, end-use industry, grade, and region. The primary application remains fertilizer production, but phosphate rocks are also used in animal feed supplements, detergents, water treatment, metal finishing, and in the production of industrial chemicals. In recent years, the market has also witnessed growing interest in alternative and specialty applications, such as in lithium iron phosphate batteries and fire retardants, though these represent a smaller share of total demand.
From a grade perspective, phosphate rock can be categorized based on phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5) content, which determines its suitability for different uses. High-grade phosphate rocks, with P2O5 content of over 30%, are especially valuable and are often exported. Low-grade deposits require beneficiation and upgrading before they can be processed effectively, leading to increased production costs.
Regionally, the Asia-Pacific region dominates the phosphate rocks market, both in terms of production and consumption. Countries like China and India are heavily reliant on phosphate-based fertilizers to maintain agricultural productivity. North America and Europe also have mature markets, though their growth is relatively slower due to environmental regulations and greater focus on sustainable farming practices. In contrast, Latin America and Africa represent emerging markets with significant growth potential, driven by agricultural expansion and increasing food demand.
One of the critical drivers of the phosphate rocks market is the growing global population. With more mouths to feed, the pressure on agriculture to produce higher yields has intensified. This has led to increased use of phosphate fertilizers, especially in regions with nutrient-deficient soils. As agricultural land becomes more limited, the emphasis on improving productivity per hectare makes the role of phosphorus even more crucial.
However, the market is not without its challenges. Environmental concerns related to phosphate mining and fertilizer use are becoming more pronounced. The mining process often results in habitat destruction, water pollution, and waste generation. Moreover, excessive use of phosphate fertilizers can lead to eutrophication in water bodies, affecting aquatic life and water quality. These concerns are prompting regulatory authorities in many countries to impose stricter guidelines, potentially affecting production and consumption patterns.
Another challenge is the non-renewable nature of phosphate rock. Unlike nitrogen, phosphorus cannot be synthetically produced, making phosphate rocks a finite resource. Some analysts warn of a potential "phosphorus crisis" in the coming decades, where demand could outstrip supply, leading to price volatility and geopolitical tensions. This has led to increasing interest in phosphate recycling, sustainable agricultural practices, and the development of alternative fertilizers.
Technological advancements in mining and processing techniques are helping to address some of these concerns. New methods allow for more efficient extraction, better waste management, and lower energy consumption. There is also ongoing research into phosphate recovery from wastewater and agricultural runoff, aiming to create a more circular and sustainable phosphorus economy.